2.2 The Big Picture
Although the protocol suite is called "TCP/IP,"
there are more members of this family than just TCP and IP.
Figure 2.1 shows an
overview of these protocols.
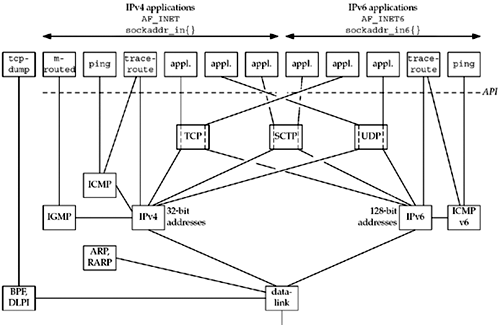
We show both IPv4 and IPv6 in this figure.
Moving from right to left, the rightmost five applications are
using IPv6; we will talk about the AF_INET6 constant in
Chapter 3,
along with the sockaddr_in6 structure. The next six
applications use IPv4.
The leftmost application, tcpdump,
communicates directly with the datalink using either the BSD packet
filter (BPF) or the datalink provider interface (DLPI). We mark the
dashed line beneath the nine applications on the right as the
API, which is normally sockets or
XTI. The interface to either BPF or DLPI does not use sockets or
XTI.
There is an exception to this, which we will
describe in more detail in Chapter 28: Linux provides access
to the datalink using a special type of socket called
SOCK_PACKET.
We also note in Figure 2.1 that the traceroute program
uses two sockets: one for IP and another for ICMP. In Chapter 28, we will
develop IPv4 and IPv6 versions of both ping and
traceroute.
We now describe each of the protocol boxes in
this figure.
|
IPv4
|
Internet Protocol
version 4. IPv4, which we often denote as just IP, has been
the workhorse protocol of the IP suite since the early 1980s. It
uses 32-bit addresses (Section A.4).
IPv4 provides packet delivery service for TCP, UDP, SCTP, ICMP, and
IGMP.
|
|
IPv6
|
Internet Protocol
version 6. IPv6 was designed in the mid-1990s as a
replacement for IPv4. The major change is a larger address
comprising 128 bits (Section A.5), to
deal with the explosive growth of the Internet in the 1990s. IPv6
provides packet delivery service for TCP, UDP, SCTP, and
ICMPv6.
We often use the word "IP" as an adjective, as in IP layer and IP
address, when the distinction between IPv4 and IPv6 is not
needed.
|
|
TCP
|
Transmission Control
Protocol. TCP is a connection-oriented protocol that
provides a reliable, full-duplex byte stream to its users. TCP
sockets are an example of stream
sockets. TCP takes care of details such as acknowledgments,
timeouts, retransmissions, and the like. Most Internet application
programs use TCP. Notice that TCP can use either IPv4 or IPv6.
|
|
UDP
|
User Datagram
Protocol. UDP is a connectionless protocol, and UDP sockets
are an example of datagram
sockets. There is no guarantee that UDP datagrams ever reach
their intended destination. As with TCP, UDP can use either IPv4 or
IPv6.
|
|
SCTP
|
Stream Control
Transmission Protocol. SCTP is a connection-oriented
protocol that provides a reliable full-duplex association. The word
"association" is used when
referring to a connection in SCTP because SCTP is multihomed,
involving a set of IP addresses and a single port for each side of
an association. SCTP provides a message service, which maintains
record boundaries. As with TCP and UDP, SCTP can use either IPv4 or
IPv6, but it can also use both IPv4 and IPv6 simultaneously on the
same association.
|
|
ICMP
|
Internet Control
Message Protocol. ICMP handles error and control information
between routers and hosts. These messages are normally generated by
and processed by the TCP/IP networking software itself, not user
processes, although we show the ping and
traceroute programs, which use ICMP. We sometimes refer to
this protocol as ICMPv4 to distinguish it from ICMPv6.
|
|
IGMP
|
Internet Group
Management Protocol. IGMP is used with multicasting
(Chapter
21), which is optional with IPv4.
|
|
ARP
|
Address Resolution
Protocol. ARP maps an IPv4 address into a hardware address
(such as an Ethernet address). ARP is normally used on broadcast
networks such as Ethernet, token ring, and FDDI, and is not needed
on point-to-point networks.
|
|
RARP
|
Reverse Address
Resolution Protocol. RARP maps a hardware address into an
IPv4 address. It is sometimes used when a diskless node is
booting.
|
|
ICMPv6
|
Internet Control
Message Protocol version 6. ICMPv6 combines the
functionality of ICMPv4, IGMP, and ARP.
|
|
BPF
|
BSD packet
filter. This interface provides access to the datalink
layer. It is normally found on Berkeley-derived kernels.
|
|
DLPI
|
Datalink provider
interface. This interface also provides access to the
datalink layer. It is normally provided with SVR4.
|
Each Internet protocol is defined by one or more
documents called a Request for Comments
(RFC), which are their formal specifications. The solution
to Exercise 2.1
shows how to obtain RFCs.
We use the terms "IPv4/IPv6 host" and "dual-stack host" to denote hosts that support
both IPv4 and IPv6.
Additional details on the TCP/IP protocols
themselves are in TCPv1. The 4.4BSD implementation of TCP/IP is
described in TCPv2.
|