8.3 UDP Echo Server: main
Function
We will now redo our simple echo client/server
from Chapter
5 using UDP. Our UDP client and server programs follow the
function call flow that we diagrammed in Figure 8.1. Figure 8.2 depicts the functions
that are used. Figure 8.3
shows the server main function.
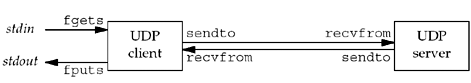
Figure 8.3 UDP
echo server.
udpcliserv/udpserv01.c
1 #include "unp.h"
2 int
3 main(int argc, char **argv)
4 {
5 int sockfd;
6 struct sockaddr_in servaddr, cliaddr;
7 sockfd = Socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
8 bzero(&servaddr, sizeof(servaddr));
9 servaddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
10 servaddr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
11 servaddr.sin_port = htons(SERV_PORT);
12 Bind(sockfd, (SA *) &servaddr, sizeof(servaddr));
13 dg_echo(sockfd, (SA *) &cliaddr, sizeof(cliaddr));
14 }
Create UDP socket, bind server's
well-known port
7鈥?2
We create a UDP socket by specifying the second argument to
socket as SOCK_DGRAM (a datagram socket in the
IPv4 protocol). As with the TCP server example, the IPv4 address
for the bind is specified as INADDR_ANY and the
server's well-known port is the constant SERV_PORT from
the unp.h header.
13 The
function dg_echo is called to perform server
processing.

|